Demystifying WAN Networks: A Beginner’s Guide
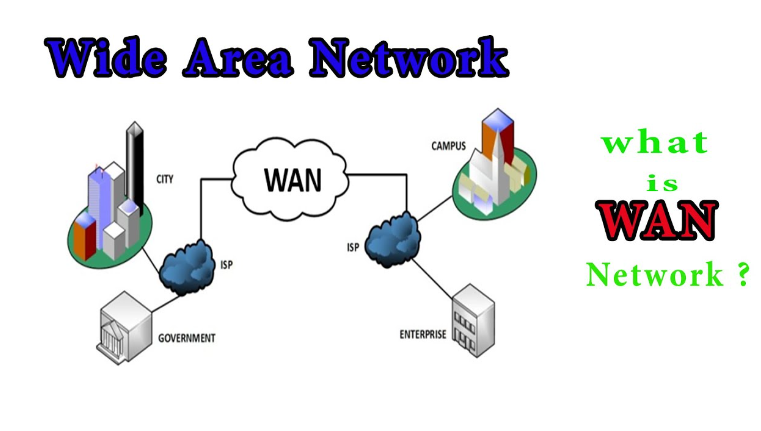
When navigating technology, grasping the frameworks that keep everyone connected becomes essential. Wide-area networks (WAN) are the backbone of global communications, linking devices across cities, countries, and continents. For those wondering what is a WAN network, it’s a technology designed to extend over large geographical areas, facilitating communication and data transfer across vast distances. This exploration aims to shed light on its complexities, making the subject accessible to novices and offering a foundational understanding of how these critical infrastructures operate.
Contents
- 1 Foundations of WAN Networks
- 2 The Architecture Behind WAN
- 3 Transmission Technologies: The Veins of WAN
- 4 Optimising Performance
- 5 Security Measures: Safeguarding Data Across Distances
- 6 Expanding to Business Needs
- 7 Quality of Service (QoS) Management
- 8 Disaster Recovery and Redundancy
- 9 Adaptation to Emerging Technologies
Foundations of WAN Networks
At its core, it encompasses a network that extends over a large geographical area. Unlike local area networks (LANs), which connect devices nearby, they facilitate data exchange over long distances. This capability supports many applications, from email communication to accessing and sharing files across corporate sites.
The Architecture Behind WAN
WAN architecture is distinguished by its ability to consolidate multiple minor connections into a cohesive system. This integration is achieved through routers and switches that direct data traffic efficiently. Understanding the infrastructure is pivotal for understanding how information travels vast distances without significant delays or loss.
Transmission Technologies: The Veins of WAN
Various transmission technologies are employed to facilitate this connectivity. These range from traditional copper wires and fibre optic cables to satellite and cellular connections. Each method offers unique advantages and limitations, influenced by transmission speed, reliability, and coverage area.
Optimising Performance
Optimising the performance of these networks involves several strategies, including traffic shaping, load balancing, and WAN optimisation appliances. These techniques enhance data flow efficiency, reduce latency, and improve reliability.
Security Measures: Safeguarding Data Across Distances
Implementing robust security measures becomes indispensable as WANs facilitate the transmission of sensitive information across public and private sectors. Encryption, firewalls, and secure VPNs are tools used to safeguard data from unauthorised permits and cyber threats.
Expanding to Business Needs
These networks are inherently designed to be scalable and flexible, accommodating the ever-expanding needs of businesses and governments. This scalability ensures that as an organisation grows, its connectivity can extend to new geographical locations without completely overhauling the existing infrastructure. Moreover, they are flexible enough to incorporate new technologies and transmission methods as they emerge. This adaptability is essential in a digital landscape where technological advancements occur quickly.
Quality of Service (QoS) Management
Quality of Service (QoS) management is a pivotal feature of this solution. It ensures that data traffic is prioritised to meet the needs of different applications and services. With QoS, critical applications such as voice over IP (VoIP) and video conferencing can be prioritised over less sensitive data. This ensures that vital communications are delivered with minimal delay and maximum clarity, essential for maintaining business operations and effective communication across global teams.
Disaster Recovery and Redundancy
WANs are integral to disaster recovery strategies, offering redundancy and data backup capabilities across geographically dispersed locations. Distributing relevant resources and data storage helps ensure that operations can continue with minimal interruption in case of a system failure or a disaster at one site.
Adaptation to Emerging Technologies
These networks have the inherent capacity to adapt and integrate emerging technologies, ensuring they remain at the forefront of digital communication infrastructure. As technological innovation continues rapidly, they are designed flexibly to embrace advancements such as 5G wireless technology, Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, and cloud computing services. This adaptability enhances the connection’s performance and reliability and ensures that it can support the evolving demands of businesses and consumers alike.
Understanding a WAN network becomes more than a matter of technical proficiency; it is a prerequisite for participating in the globalised economy. They facilitate communication and enable innovation and collaboration across continents.